Data Protection Enablement
Ensuring the Security and Integrity of Your Valuable Information

Securing Data with Immutable Snapshots
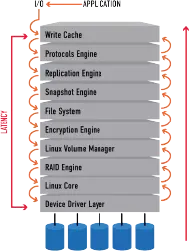
vSnap & vSnapLock
Elevating the capabilities of business analytics applications, our storage platform introduces a powerful boost in performance and scalability. By seamlessly incorporating the fastest media available, such as SCM drives, we enable accelerated data access and processing. The architecture’s scalability ensures that growing data volumes and heightened processing demands are effortlessly accommodated, thus guaranteeing the efficiency of all analytics operations.
Safeguarding the integrity of critical analytics data, our advanced data protection features, including snapshotting and replication, stand as robust safeguards. Moreover, the platform’s ingenuity in cost optimization ensures that storage resource management is not only intelligent but also cost-effective, without compromising on performance.
This performance-driven solution redefines high-performing storage for analytics workloads, equipping businesses with the reliability and power they need.
vReplicate
Our data replication technology is uniquely engineered to operate smoothly across dissimilar hardware. This allows you to tailor your replication strategy, be it synchronous or asynchronous, or one-to-one or one-to-many, across varying storage types. Should a failure occur at your primary site, you can swiftly transition to the replicated data at a secondary location, reducing downtime and ensuring business continuity. This feature underscores our commitment to robust, adaptable data management.
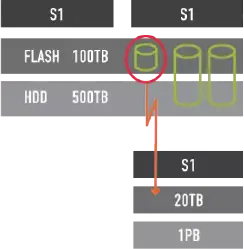
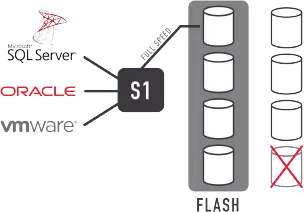
vRAID
Our cutting-edge RAID technology enhances data protection through advanced features such as performant erasure coding and distributed parity. These measures safeguard against drive failures and enable efficient data reconstruction when disk errors occur. Another advantage we offer is the optimization of storage efficiency. Unlike traditional systems that require dedicated parity drives, our solution maximizes usable capacity by distributing data and parity across multiple drives, thereby reducing costs and driving performance. Furthermore, our scalable configurations allow for a custom-tailored approach to data protection, supporting various RAID levels to meet specific needs and performance demands.
